MRSA Nasopharyngeal Swab Screening: A Crucial Step in Infection Control

Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a serious bacterial infection that poses a significant threat in healthcare environments. By detecting MRSA colonization through nasopharyngeal swabs, we can identify individuals carrying the bacteria and take appropriate preventive measures.
What are the Benefits of Nasopharyngeal Swab Testing for MRSA?
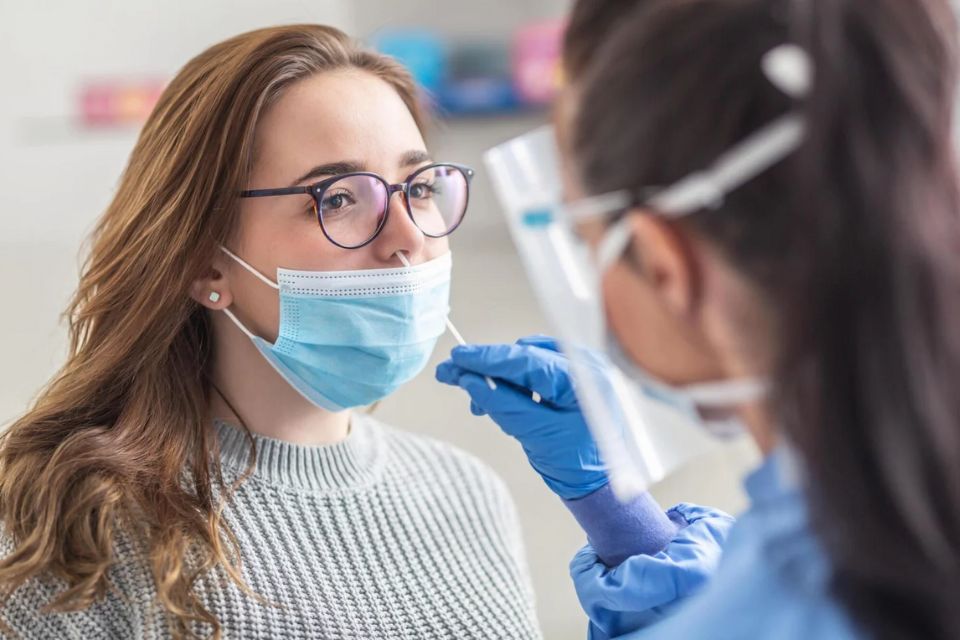
The primary sites of MRSA colonization are the nares and throat. Nasopharyngeal swabs offer a relatively non-invasive and convenient method for detecting MRSA presence in the body. Compared to other invasive testing methods, nasopharyngeal swabs are less traumatic and easier to perform, making them a commonly used screening tool for MRSA.
How is the MRSA Nasopharyngeal Swab Testing Procedure Conducted?
According to the study described in the paper, researchers performed nasopharyngeal swab sampling on 855 patients between June 2014 and May 2015 at Trogir Hospital in Croatia. The swabs were placed in a soap solution, and subsequent bacterial culture, isolation, and identification were performed to determine the presence of MRSA.
What is the Relationship Between MRSA Colonization and Infection?
The data showed that out of the 855 patients, 117 (13.7%) were MRSA carriers. Among these MRSA-colonized individuals, 27 (23.1%) developed MRSA-related infections, affecting the skin and soft tissue (16 cases), bloodstream (5 cases), bones (4 cases), and urinary tract (2 cases). This finding highlights the association between MRSA colonization and infection, underscoring the importance of timely detection and prevention.
What are the Major Risk Factors for MRSA Colonization?
The study also identified several factors that may increase the risk of MRSA colonization, such as advanced age, prolonged bed rest, diabetes, and recent hospitalization history. Healthcare facilities should pay particular attention to these high-risk groups and implement targeted preventive measures to reduce the spread of MRSA within the institution.
How Can the Spread of MRSA in Healthcare Settings be Effectively Controlled and Prevented?
The transmission of MRSA is often linked to nosocomial infections and the overuse of antibiotics. Therefore, strengthening infection control practices and promoting the judicious use of antibiotics are crucial. Additionally, regular nasopharyngeal swab screening of healthcare workers and high-risk patients, followed by isolation of positive cases, can help curb the spread of MRSA in healthcare environments.
Click to View → Mantacc 96000A Nasopharyngeal Swab
References
Nasal-Swab Results for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Associated Infections